Info G Innovative Solutions is a leading provider of all types of LIDAR data labeling services. We provide LIDAR point cloud grading, and our team is committed to utilizing state-of-the-art algorithms and automation to help streamline the annotation process. From surveying and mapping to aerospace, geospatial intelligence, industrial process control, robotics, mining, and measuring earth volumes for building construction.
LIDAR is a fundamental element for the success of self-driving cars. The 3D perception capabilities provide clear information about the surrounding environment and it’s vital to avoid running into obstacles like pedestrians and other vehicles.
Unlock the potential of your LIDAR data with our expert labeling services!
We make your data go further. Whether you need high-quality laser point clouds for creating maps, training autonomous vehicles, or extracting feature engineering for machine learning, we're the fastest and most accurate path to your goal with the following methods.
High-quality video annotation generates ground truth datasets for optimal machine learning functionality. There are numerous deep learning applications for video annotation across industries including self-driving cars, medical AI, and geospatial technology.
It is the process of labeling or tagging video clips which are used for training computer vision models to detect or identify objects. Unlike image annotation, video annotation involves annotating objects on a frame-by-frame basis to make them recognizable for machine learning models.
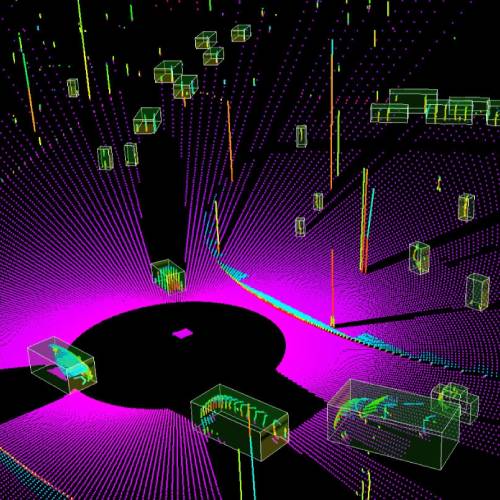
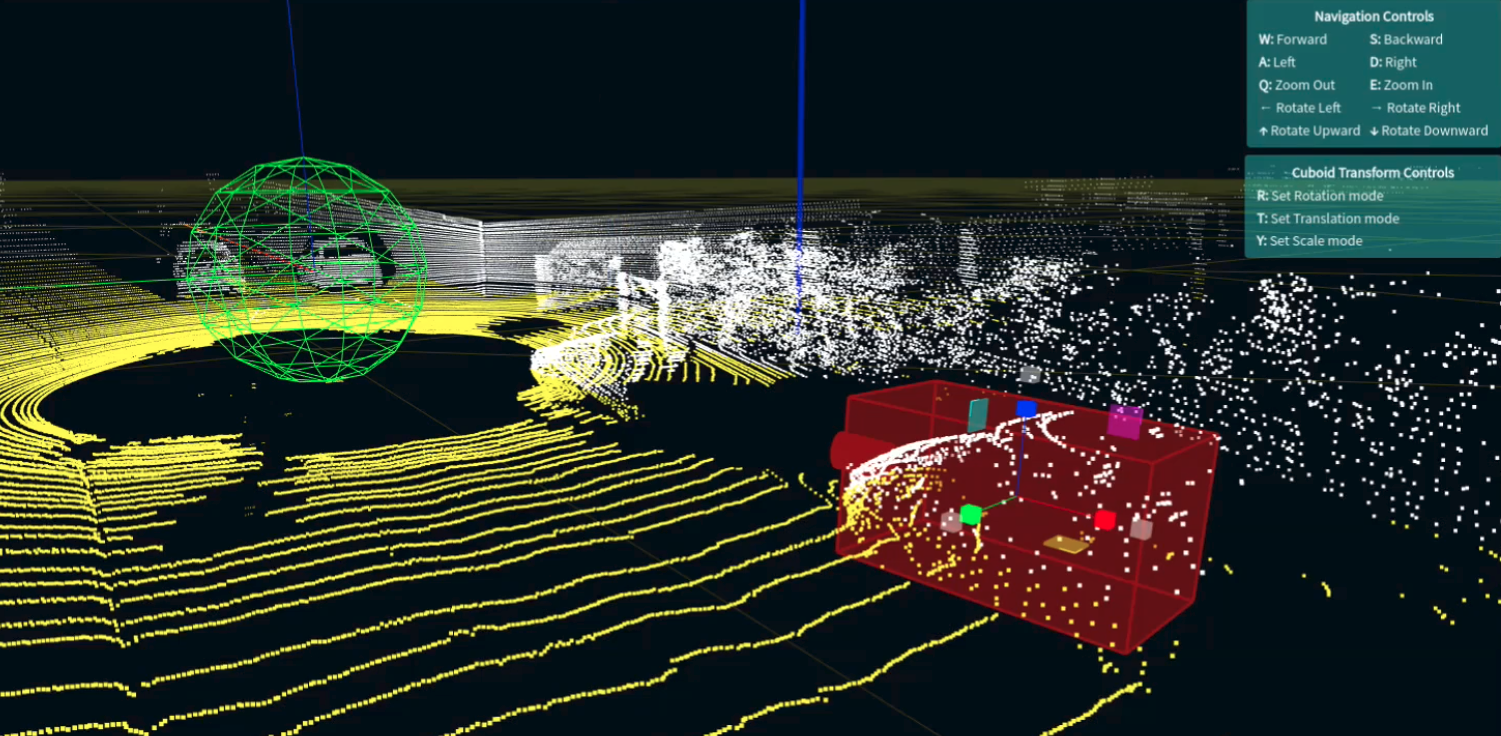

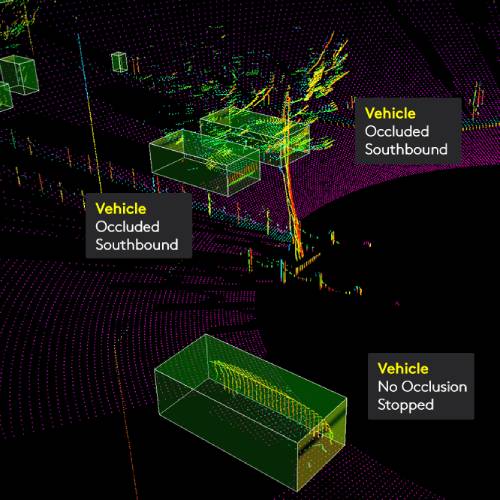
Laser
Sends pulses of light towards objects (usually ultraviolet or near-infrared).
Scanner
Regulates the speed at which the laser can scan target objects and the maximum distance reached by the laser.
Sensor
Measures the time it takes for the light from the laser to bounce off the target object and return to the system (thereby measuring distance).
GPS
Tracks the location of the LiDAR system to ensure accuracy of the distance measurements.
